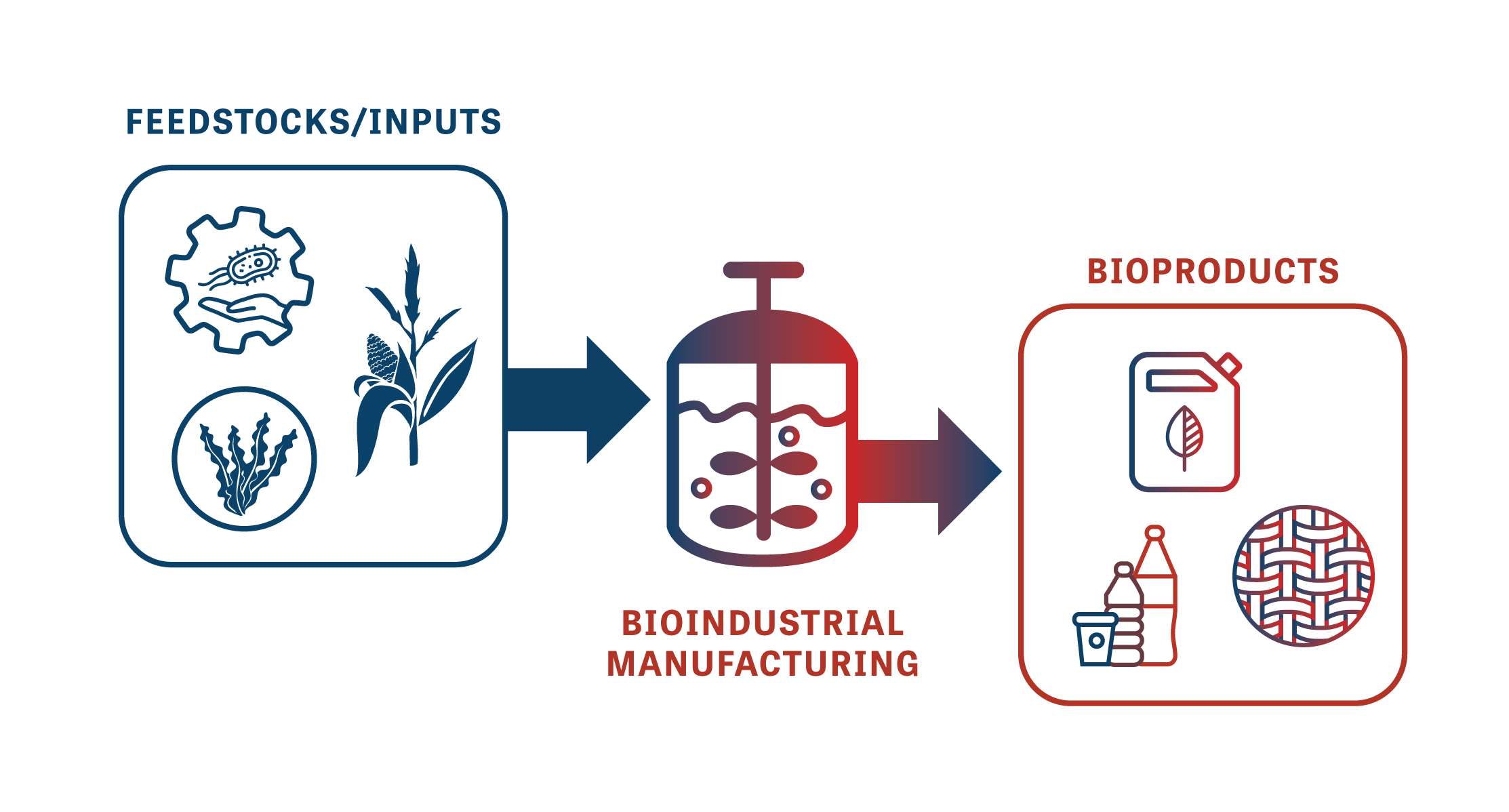
Bioindustrial Manufacturing
BioMADE unleashes the power of biology to help create and domestically source the manufactured goods that people use every day. Up to 60% of materials in the global consumer product supply chain can be produced using biology and by 2030, most people on the planet will have consumed, worn, or been treated by a product of emerging biotechnology.
Bioindustrial manufacturing uses biological systems to convert agricultural feedstocks and waste streams to high-value chemicals, materials, textiles, fuels, bioplastics, and other products. Because bioindustrial manufacturing typically uses feedstocks such as corn, soy, and sugar beets, American farmers will benefit from the new markets created by BioMADE technologies, and rural communities will benefit from the manufacturing jobs creating the associated products.
Biotechnology and bioindustrial manufacturing are not new concepts – fermentation was first harnessed by humans over 10,000 years ago and is used to produce products like cheese, yogurt, and beer. Today, innovative U.S. companies are taking this to the next level and unlocking a new future where everyday chemicals, materials, plastics, textiles, and more are safely manufactured in the U.S. using biology.
The U.S. bioeconomy is currently worth at least $950 billion – and growing every day. That’s more than 5% of U.S. GDP. BioMADE supports its members to create marketable products through bioindustrial manufacturing, further catalyzing this domestic economic growth. Bioindustrial manufacturing has the potential to impact all sectors of the economy and all areas of society, helping the U.S. become more self-sufficient and sophisticated in manufacturing.
Consumer Applications
Plant-based nylon and other durable textiles and fibers for clothing and shoes
Biodegradable plastics and compostable packaging materials
Bio-butanediol used to make spandex, compostable tote bags, coffee capsules, food packaging, and more
Probiotics, fragrances, beauty and personal care items
Healthier cooking oils and sweeteners, and more nutrient-dense infant formula
Critical minerals that go into cell phones and semiconductors
Everyday products like fertilizers, detergents, paints and coatings, and adhesives
Photos below © Algenesis, Cambium, Amyris, Eco-Shot, Debut Biotech, Biomason, Geno, Novonesis
Defense Applications
Novel and performance-driven chemicals, materials, and textiles
Natural rubber made from dandelions
High-performance aviation fuels
Bio-based laser eyewear protection
Anti-corrosives, lubricants, adhesives, and sealants
Thermal coatings, high temperature-resistant foams, and thermal protection systems
Energetics and energetic precursors
Deployable production of fuels, lubricants, and other critical materials
Rapid, point-of-need infrastructure production with biocement
Lightweight composite materials, shotgun wads, and ammunition links
Other needed supplies that could be produced on-site at point-of-need – reducing vulnerable convoys – and that degrade quickly so as to not compromise warfighter position
Benefits of Bioindustrial Manufacturing
Enhances national security by creating more robust and resilient domestic supply chains
Protects and enhances warfighters
Creates needed products and materials without foreign inputs
Re-shores manufacturing jobs and establishes the U.S. as a self-sufficient and global manufacturing leader
Builds a globally competitive STEM workforce
Supports American farmers and enhances rural development